An ankle sprain occurs when the ligaments around the ankle joint are stretched or torn, typically from a sudden twist, turn, or fall. It is one of the most common injuries, particularly in athletes. Additionally, syndesmotic injuries, also known as high ankle sprains, can occur when the ligaments connecting the tibia and fibula (syndesmosis) are injured, typically from rotational force or severe twisting of the ankle. Our expert San Francisco sports podiatrist, Dr. Cates, offers compassionate, professional care to get you back on your feet.

Ankle Sprains
Causes and Risk Factors
Causes and Risk Factors include activities that involve running, jumping, or sudden changes in direction. Risk factors include previous ankle sprains, high arch foot, weak or imbalanced muscles, and improper footwear.
Symptoms
Symptoms include pain, swelling, bruising, and limited mobility of the ankle joint. Severe sprains may result in instability or difficulty walking.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis involves a physical exam to assess the extent of pain and swelling. X-rays are used to rule out fractures, and an MRI may be needed to evaluate soft tissue damage or severe ligament injuries.
Treatment
Treatment typically includes the RICE method (rest, ice, compression, elevation) for mild sprains. More severe cases may require immobilization with a brace or boot, physical therapy, or in rare cases, surgery to repair torn ligaments.

Turf Toe
Turf toe is a sprain of the big toe joint (metatarsophalangeal joint), caused by hyperextension. It often occurs when the toe is forced upward while the foot is planted.
Causes and Risk Factors include activities like football, soccer, or basketball, especially with cleats or playing on artificial turf.
Symptoms include pain, swelling, and stiffness at the base of the big toe, particularly during activities involving pushing off the foot. Bruising may also occur.
Diagnosis is usually made through a physical examination, and imaging like X-rays or MRI may be used to rule out fractures or assess severe damage.
Treatment typically involves rest, ice, and elevation. A boot or brace may be used for immobilization in severe cases, and physical therapy may be recommended for recovery. Our premier San Francisco sports podiatrist will curate a custom treatment plan to ensure your recovery is smooth.
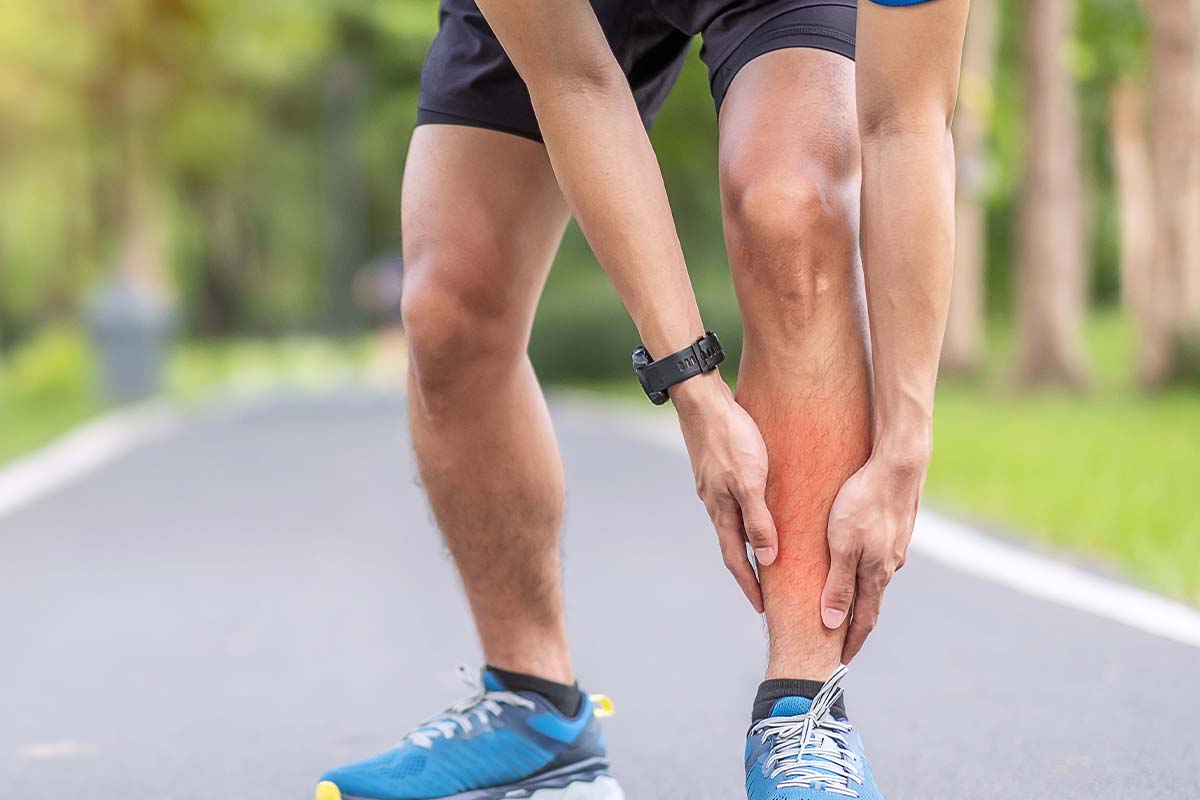
Shin Splints
Shin splints, or medial tibial stress syndrome, is pain along the shin bone, typically caused by repetitive stress during running or jumping.
Causes and Risk Factors include overuse from high-impact activities, improper footwear, flat feet, or sudden increases in training intensity.
Symptoms include a dull, aching pain along the inside of the shin that may worsen during physical activity and improve with rest.
Diagnosis is based on a physical examination. X-rays may be used to rule out fractures, and an MRI may help assess soft tissue damage.
Treatment includes rest, ice, NSAIDs, and proper footwear. Stretching and strengthening exercises may help, and in some cases, physical therapy or activity modification is recommended.
Exertional Compartment Syndrome
Exertional compartment syndrome is a condition where increased pressure within a muscle compartment, usually in the lower leg, restricts blood flow and causes pain during exercise.
Causes and Risk Factors include prolonged or intense physical activity, especially in athletes involved in running or jumping sports. Risk factors include tight muscles, overuse, or tight fascia, which can limit the space within the muscle compartments and increase pressure. This tightness can restrict blood flow to the muscles during exercise, leading to pain and discomfort. A professional sports podiatrist can work with you to help come up with preventative measures to minimize the risk of developing Exertional compartment syndrome.
Symptoms include pain, swelling, and tightness in the lower leg during physical activity, often subsiding with rest but recurring with exertion.
Diagnosis involves a physical examination and measurement of pressure within the affected muscle compartment. Compartment pressures can be measured both at rest and following activity to definitively diagnose the condition, as pressures often rise during exercise and remain elevated after exertion.
Treatment may involve rest, ice, NSAIDs, and reducing activity levels. In severe cases, surgical release of the affected compartment / fascia may be necessary. In these cases, I employ minimally invasive surgical techniques to decrease complications and help patients return to activity sooner.

Lisfranc Injuries
A Lisfranc injury involves damage to the midfoot ligaments and bones, often caused by trauma or twisting motions. It is a serious injury that may require surgical intervention.
Causes and Risk Factors include falls, direct impacts, or high-energy twisting injuries during sports like football, soccer, or basketball.
Symptoms include pain in the midfoot, swelling, and bruising. There may be difficulty bearing weight or walking.
Diagnosis is typically made through a physical exam, and imaging such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI is essential for confirming the injury and determining its severity.
Treatment may involve conservative methods like rest, ice, and immobilization in a boot or cast for minor injuries. Severe injuries may require surgical intervention to stabilize the bones and ligaments in the midfoot.
Contact Dr. Cates, a highly-rated San Francisco sports podiatrist, for a personalized consultation.

